Linux是一个强大而复杂的操作系统,它可以运行在各种硬件和环境中,提供各种功能和服务。但是,Linux也需要定期地进行健康检查,以确保系统的正常运行和性能。Linux有很多内置的命令和工具可以用来检查系统的状态和参数,但是这些命令和工具可能需要手动地输入和执行,比较繁琐和耗时。本文将介绍如何使用Bash脚本来编写一个简单而实用的Linux健康检查工具,可以一键地检查系统的基本信息、资源使用情况、网络连接情况等。
编写脚本
$ vim linuxmi
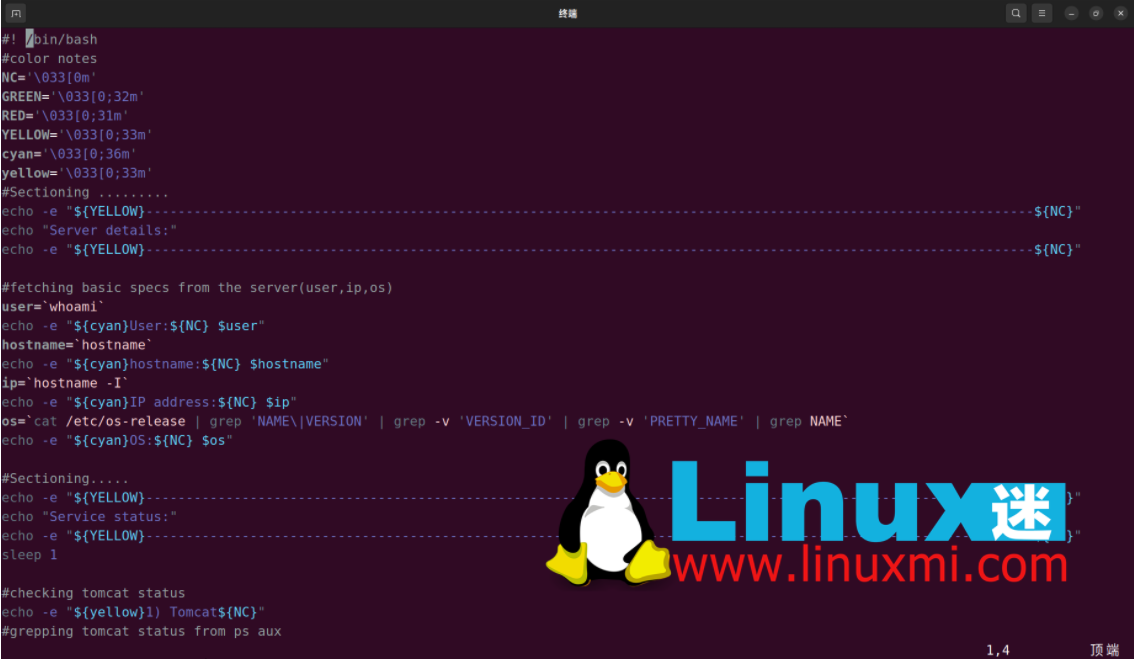
#! /bin/bash
#color notes
NC='\033[0m'
GREEN='\033[0;32m'
RED='\033[0;31m'
YELLOW='\033[0;33m'
cyan='\033[0;36m'
yellow='\033[0;33m'
#Sectioning .........
echo -e "${YELLOW}----------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------${NC}"
echo "Server details:"
echo -e "${YELLOW}---------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-${NC}"
#fetching basic specs from the server(user,ip,os)
user=`whoami`
echo -e "${cyan}User:${NC} $user"
hostname=`hostname`
echo -e "${cyan}hostname:${NC} $hostname"
ip=`hostname -I`
echo -e "${cyan}IP address:${NC} $ip"
os=`cat /etc/os-release | grep 'NAME\|VERSION' | grep -v 'VERSION_ID' | grep -v
'PRETTY_NAME' | grep NAME`
echo -e "${cyan}OS:${NC} $os"
#Sectioning.....
echo -e "${YELLOW}-------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------${NC}"
echo "Service status:"
echo -e "${YELLOW}-------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------${NC}"
sleep 1
#checking tomcat status
echo -e "${yellow}1) Tomcat${NC}"
#grepping tomcat status from ps aux
pp=`ps aux | grep tomcat | grep "[D]java.util"`
if [[ $pp =~ "-Xms512M" ]];then
echo -e " Status: ${GREEN}UP${NC}"
else
echo -e " Status: ${RED}DOWN${NC}"
fi
echo ""
#function to check apache is running or
not!
function apache(){
echo -e "${yellow}2) Apache-httpd${NC}"
#grepping apache status from ps aux
httpd=`ps aux | grep httpd | grep apache`
if [[ $httpd =~ "apache" ]];then
echo -e " Status: ${GREEN}UP${NC}"
else
echo -e " Status: ${RED}DOWN${NC}"
fi
}
#function to check elastic is running or not
function elastic(){
echo -e "${yellow}3) Elasticsearch${NC}"
#grepping elasticsearch status from ps aux
elastic=`ps aux | grep elasticsearch`
if [[ $elastic =~ "elastic+" ]];then
echo -e " Status: ${GREEN}UP${NC}"
else
echo -e " Status: ${RED}DOWN${NC}"
fi
#function to check mysql is running or not
}
function mysql(){
echo -e "${yellow}4) Mysql${NC}"
#grepping mysql status from ps aux
mysql=`ps aux | grep mysqld`
if [[ $mysql =~ "mysqld" ]];then
echo -e " Status: ${GREEN}UP${NC}"
else
echo -e " Status: ${RED}DOWN${NC}"
fi
}
function docker(){
echo -e "${yellow}5) Docker${NC}"
#grepping docker status from ps aux
docker=`systemctl status docker | grep dead`
if [[ $docker =~ "dead" ]];then
echo -e " Status: ${GREEN}UP${NC}"
else
echo -e " Status: ${RED}DOWN${NC}"
fi
}
#calling functions
apache
echo ""
elastic
echo ""
mysql
echo ""
docker
echo ""
#Sectioning............
#Fetching mem and cpu informations
echo -e "${YELLOW}--
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------${NC}"
echo "Memory Details:"
echo -e "${YELLOW}----------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------${NC}"
sleep 1
#view mem info
free -h
#get uptime details
uptime=$(uptime | awk '{print $3,$4}' | cut -f1 -d,)
echo -e "${cyan}System Uptime:${NC} :$uptime"
#Fetching the load average
loadaverage=$(top -n 1 -b | grep "load average:" | awk '{print $10 $11 $12}')
echo -e "${cyan}Load average:${NC}: $loadaverage"
echo -
e "${cyan}The top 10 services with high resource usage are listed below.${NC}"
#Get
top services with high resource utilization
ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu --sort=-%mem | head
#sectioning...........
#Fetching server space details!
echo -e "${YELLOW}--------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-${NC}"
echo "Server space Details:"
echo -e "${YELLOW}--------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------
-${NC}"
#View disk space details
df -h
echo "-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------"
2、我们可以将该脚本转换为全局命令,将文件移动到 sbin 目录,并赋予执行权限。
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com
% sudo cp linuxmi /usr/sbin/
[sudo] linuxmi 的密码:
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com
% sudo chmod +x /usr/sbin/linuxmi
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com
3、现在您可以在 shell 的任何位置调用该脚本。
linuxmi@linuxmi ~/www.linuxmi.com
% linuxmi
示例输出如下:


优势
-
只需一个命令就可以轻松访问完整的服务器信息,并且还可以在出现问题时安排警报通知。 -
编辑脚本并添加服务非常简单。 -
显示有关正在运行的进程、磁盘空间、宕机时间、内存详细信息、高进程列表等的详细信息。
以上就是良许教程网为各位朋友分享的Linu系统相关内容。想要了解更多Linux相关知识记得关注公众号“良许Linux”,或扫描下方二维码进行关注,更多干货等着你 !



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
 支付宝扫一扫打赏
支付宝扫一扫打赏

.png)
